Multiple myeloma is associated with more laboratory abnormalities than any other disease. Some of the notable ones are:
Blood
- Peripheral blood smear: normocytic, normochromic anemia, macrocytic anemia, rouleaux formation, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, abnormal plasma cells (15%)
- High Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
- High serum total protein and low albumin/globulin ratio
- Septicemia: especially from encapsulated organisms, which are normally cleared by the spleen with the aid of well-functioning antibodies.
Kidney
- Renal failure: ↑ BUN and creatinine, metabolic acidosis
- Anion gap: normal, high or low anion gap
- Nephrotic syndrome: hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, proteinuria (elevated protein on urine dipstick, elevated urine protein to creatinine ratio), lipiduria (look for Maltese cross formations under polarized light microscopy), peripheral edema
- Proximal (Type 2) renal tubular acidosis: hypokalemia, low urine pH, non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
- Acquired Fanconi syndrome: hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, Proximal (Type 2) renal tubular acidosis, phosphaturia, aminoaciduria, glucosuria on urinalysis with a normal blood glucose
- Distal (Type 4) renal tubular acidosis: hyperkalemia, non-anion gap metabolic acidosis, ↑ urinary anion gap, ↓ urine pH, ↓ renin, low-normal aldosterone levels and blood pressure
Electrolytes
- ↓ Sodium
- ↑Calcium
- ↑ or ↓ potassium
Other
- ↑ Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
- Hypogammaglobulinemia: ↓ levels of normal immunoglobulins IgG, IgA and IgM
- ↑ Alkaline phosphatase: if seen, should make one suspect pathological fractures
- Cryoglobulinemia: proteins, generally immunoglobulins, that precipitate out of solution in low temperatures
- Hyperviscosity (from paraproteinemia, and yes, there is a test for that!)
- Hyperuricemia
- Hyperammonemia
- Endocrinopathies
You confirm the diagnosis with:
- Serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) and immunofixation: the SPEP “spike” quantifies the amount of paraprotein, or M-protein, that is coming from a single clone of plasma cells. Immunofixation qualifies the immunoglobulin as IgG, IgA, etc.
- Urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP) and immunofixation
- Serum free light chain assay: Serum free light chains are light chains which are free of heavy chains. This is abnormal when found in the blood in large quantities. Urinary light chains are called Bence-Jones protein
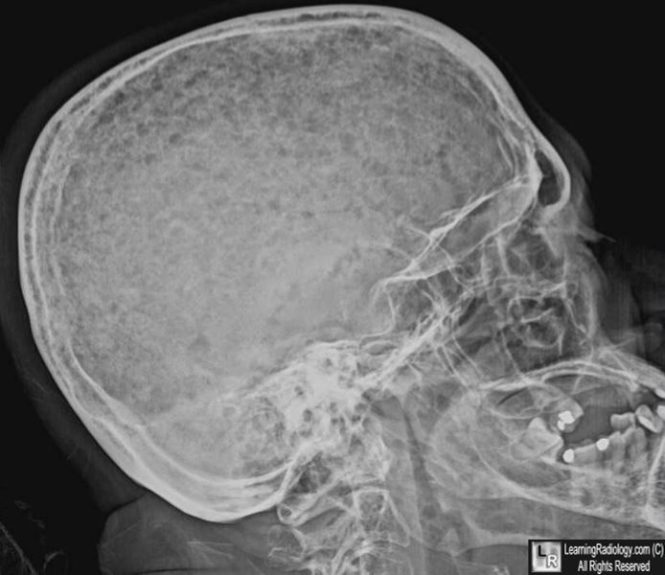
- Skeletal survey (plain radiographs, showing “punched out” lesions)

Numerous “punched out” lesions in a patient with multiple myeloma. Published with permission from LearningRadiology.com. - Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
Tumor burden is followed by:
- Beta-2 microglobulin
- LDH
References
- The Merck Manual for Health Care Professionals (accessed 5/9/2013)
- Sabatine, Marc S., MD, Pocket Medicine, 4e (2010)
- Victor Hoffbrand, Essential Haematology, 6e (2011)

Leave a Reply