Category: Emergency Medicine
-
A Visual Guide to ECG Interpretation (2017)
The current edition of A Visual Guide to ECG Interpretation (2017), much like the previous one (which I reviewed elsewhere), is a marked-up atlas of important, must-be-able-to-interpret-correctly electrocardiograms. Almost every important ECG that you can think of can be found here: coronary ischemia and occlusion, hyperkalemia, Brugada pattern, Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern, Wellens sign, arrhythmogenic right ventricular…
-
The Chief Complaint (2014)
The Chief Complaint (2014) is ideal for junior trainees and advanced medical students who are on an emergency medicine rotation and want to contribute to high acuity patient care without losing their bearing. What’s best, you can download it for free onto your mobile device.
-
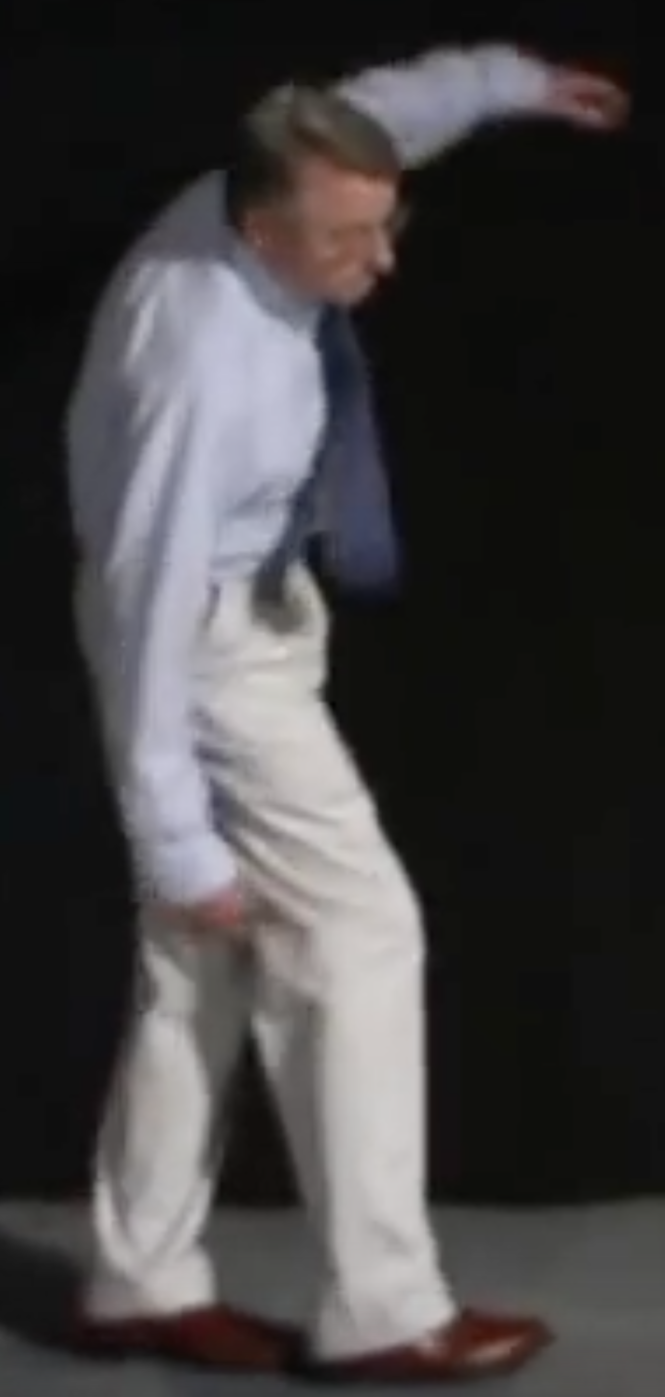

Ataxia: The Physical Examination
Ataxia is an extremely important clinical sign that has a broad and important differential diagnosis. Causes of ataxia include posterior circulation strokes and various toxic and metabolic insults to the cerebellum (and sometimes to the spinocerebellar tracts). Ataxia can be a very subtle physical finding, especially when you don’t know what to look for or…
-

Central vs. Peripheral Vertigo Simplified
The first and most important step in evaluating a patient with vertigo is to attempt to distinguish vertigo of central origin from vertigo of peripheral origin because the management of central vertigo (brain imaging, hospital admission) is very different from the management of peripheral vertigo (symptomatic treatment, outpatient referral). Differences Between Central and Peripheral Vertigo Peripheral Vertigo…
-
Stroke & TIA Mimics
Here are the important stroke and TIA mimics: Systemic and metabolic insults: especially hypoglycemia, but also a very wide variety of other systemic insults such as infections (urinary tract infections, pneumonia) and toxins, all of which can cause re-expression of symptoms of old strokes. Peripheral neuropathies such as idiopathic seventh cranial nerve (Bell’s) palsy, peripheral…
-
Headache: The Ominous Causes
Introduction Most headaches are benign and do not require a specific workup. Here are the ominous ones that require a specific workup and management. From the Patient History Sudden, severe, and maximal at onset, especially in an older patient without a prior history of headaches → subarachnoid hemorrhage → get a head CT without contrast → CT angiogram or…
-
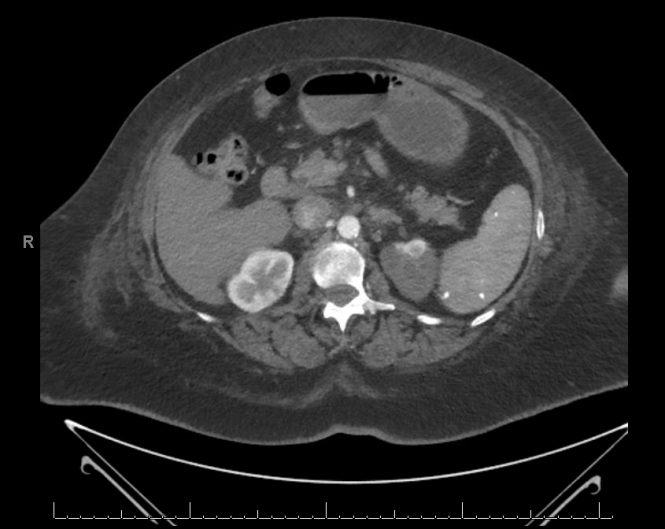
Medical Question: Flank Pain
A 60-year-old female presents to the emergency department complaining of intense left sided-flank pain radiating to the groin. Urinalysis is positive for gross hematuria, while a non-contrast CT of the abdomen and pelvis is negative for stones. The patient is sent for a contrast CT of the abdomen and pelvic, from which the following image is…