Category: Internal Medicine
-
Hematologic Emergencies
White cell disorders Tumor lysis syndrome → allopurinol, hemodialysis Leukostasis (leukemia patient with very high white cell count and neurological changes) → leukophoresis Acute hyperviscosity syndrome (in Waldenström macroglobulinemia) → plasmapheresis Red blood cell disorders Methemoglobinemia → oxygen, methylene blue Sickle cell emergencies: Acute calculous cholecystitis → antibiotics, consider surgical intervention Acute splenic sequestration crisis (shock, LUQ pain, acute…
-

Book Review: Atlas of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology (2007)
Atlas of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology (2007) by Wallace Peters and Geoffrey Pasvol offers a bleak and sometimes depressing window into the state of health, or lack thereof, of underdeveloped countries, particularly those in Africa. The names of the diseases and symptoms are fearsome and sometimes curious: dengue, blackwater fever, rabies, leprosy, bubonic plague and more. The…
-
Weakness: An Approach
As a first step, neuromuscular weakness should be distinguished from its mimics, which are: Mental fatigue bradykinesia Decreased range of motion Depression Movement limited by pain. “Abnormal fatigability of striated muscle is the cardinal manifestation of disorders of the neuromuscular junction. Exercise-dependent weakness often affects the extraocular muscles first, causing ptosis or diplopia, as the…
-
Toxic Hepatitis and Jaundice
Here are some important causes of toxic hepatitis and jaundice (notorious ones are in bold): Hepatocellular (elevated ALT and AST only): acarbose, acetaminophen, allopurinol, amiodarone, aspirin (in Reye’s syndrome), baclofen, bupropion, fluoxetine, HAART drugs, isoniazid, ketoconazole, lisinopril, losartan, methotrexate, NSAIDs, omeprazole, paroxetine, pyrazinamide, rifampin, risperidone, sertraline, statins, tetracyclines, trazodone, trovafloxacin, valproic acid, Vitamin A. Herbals…
-
An Internal Medicine Approach to Abnormal Liver Chemistry Studies
Causes of liver damage include: Toxic Acute alcoholic hepatitis (fever, leukocytosis, abnormal liver chemistry studies) acetaminophen Amanita poisoning (history of mushroom ingestion) Other drugs Infectious Viruses HAV (food-related outbreak with a relatively short incubation period) HBV HCV HEV (Pregnant patient from Southeast Asia with oro-fecally transmitted fulminant hepatitis with a very long (8 week) incubation period) CMV (teenager…
-

Electrocardiography: A Curriculum for Self-Guided Learners
“If you think there’s another specialist who has all the answers, someone else who’s going to bail you out of trouble every time you have a question about ECGs, you are mistaken. That person may just as likely be wrong, so YOU must strive to become THE expert.” Amal Mattu MD, ECG Interpretation of STEMI:…
-
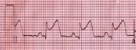
How to distinguish pericarditis from STEMI
The Problem Diffuse, convex (up) ST segment elevations with or without PR-segment depressions can be seen in both pericarditis or ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI), particularly if the patient has a wraparound LAD which supplies the inferior wall. So how can one reliably distinguish pericarditis from STEMI? The Solution If any of the following are present, a STEMI…